Author links open overlay panel
College of Textile and Clothing Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China. Jiangsu Engineering Research Center of Textile Dyeing and Printing for Energy Conservation, Discharge Reduction and Cleaner Production (ERC). China National Textile and Apparel Council Key Laboratory of Natural Dyes.Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China.School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, 99 Shangda Road, Baoshan, Shanghai 200444, China
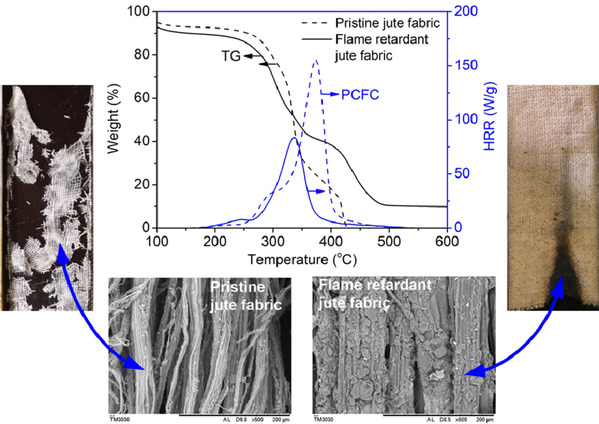
Jute is a low-cost lignocellulosic fiber, and can be applied as upholstery fabrics and composites in automotive, transport and architecture industries. Such applications have flame retardant requirements for jute fiber. In the present work, jute fabric was treated using two natural polysaccharides (chitosan [CH] and sodium alginate [SA]) for enhanced flame retardancy. Firstly, the gel was prepared through the ion-ion interaction between positively charged CH and negatively charged SA with the use of sodium chloride as stabilizing and reinforing agents. Afterwards, the CH/SA gel was used to treat jute fabric using the immersing-padding-drying approach. The thermal degradation, char-forming and heat release properties of the treated fabric were studied by thermogravimetric analysis, scanning electron microscope and pyrolysis combustion flow calorimetry. The treated jute fabric by the gel prepared using 3% w/v CH, 7% w/v SA, and 8.8% w/v sodium chloride had a limiting oxygen index of 27% and a damaged length of shorter than 5 cm in the vertical combustion, and its heat release capability was decreased by 50%.
Volume 196, February 2022, 109826
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109826

